Computer Modelling
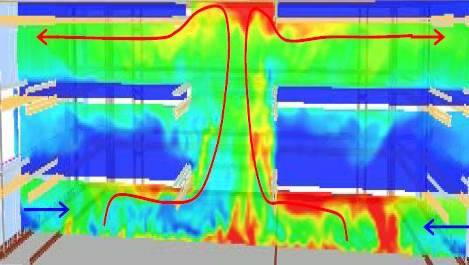
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) modelling of fire and smoke spread has become an increasingly important analytical tool for designing and demonstrating compliance of smoke management systems. As the understanding of physical phenomena such as fire dynamics, heat transfer and fluid flow increases, so does the ability to accurately model fires. This, coupled with more advanced computer algorithms coupled with modern processor speeds and memories, has massively increased the accuracy of CFD fire modelling. This allows for accurate description of fires in complex geometries, and the ability to incorporate and predict a wide range of physical fire phenomena. This is considered to be the only alternative without actually setting the building on fire to validate a smoke management system and demonstrate that the life safety objectives of the code are satisfied.
A CFD study can be undertaken using Fire Dynamics Simulator (FDS) to provide an engineered smoke management system to demonstrate compliance with the Code and local authority requirements. This tool can be used rationalize the smoke management system in regards to smoke exhaust capacity, make-up air requirements and size of smoke zones.
However, in certain situations it is necessary to predict the time needed to evacuate a building. This Evacuation Modelling can be used in combination with smoke modelling (CFD), which can predict the time available before untenable conditions are reached. The combination of these techniques is often useful in unusual or complex buildings where the standard design guides would be inappropriate, or compliance is impractical to achieve.
Examples Projects;
Al Maryah Island Tunnel (Peer Review)

Abu Dhabi Marina Mall

